퍼-즐
퍼-즐
백준 1525번 문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1525
1525번: 퍼즐
세 줄에 걸쳐서 표에 채워져 있는 아홉 개의 수가 주어진다. 한 줄에 세 개의 수가 주어지며, 빈 칸은 0으로 나타낸다.
www.acmicpc.net
1. 문제
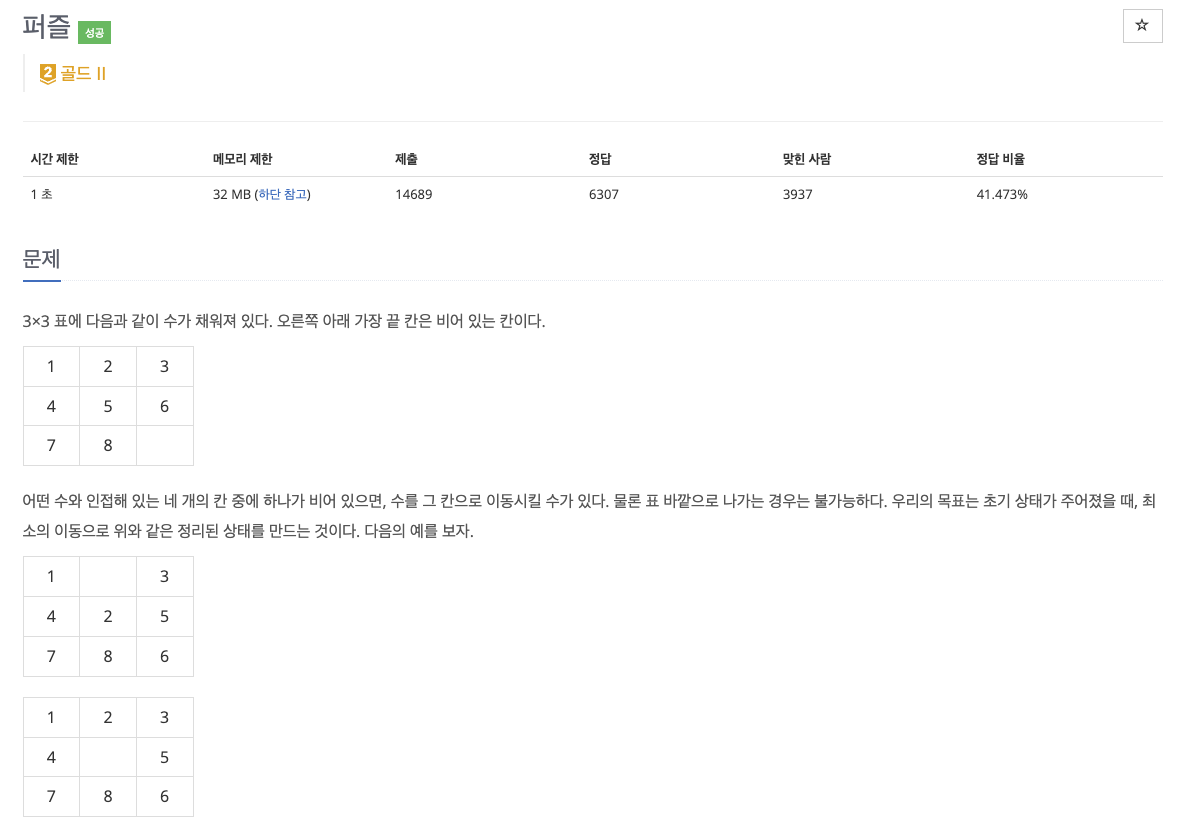
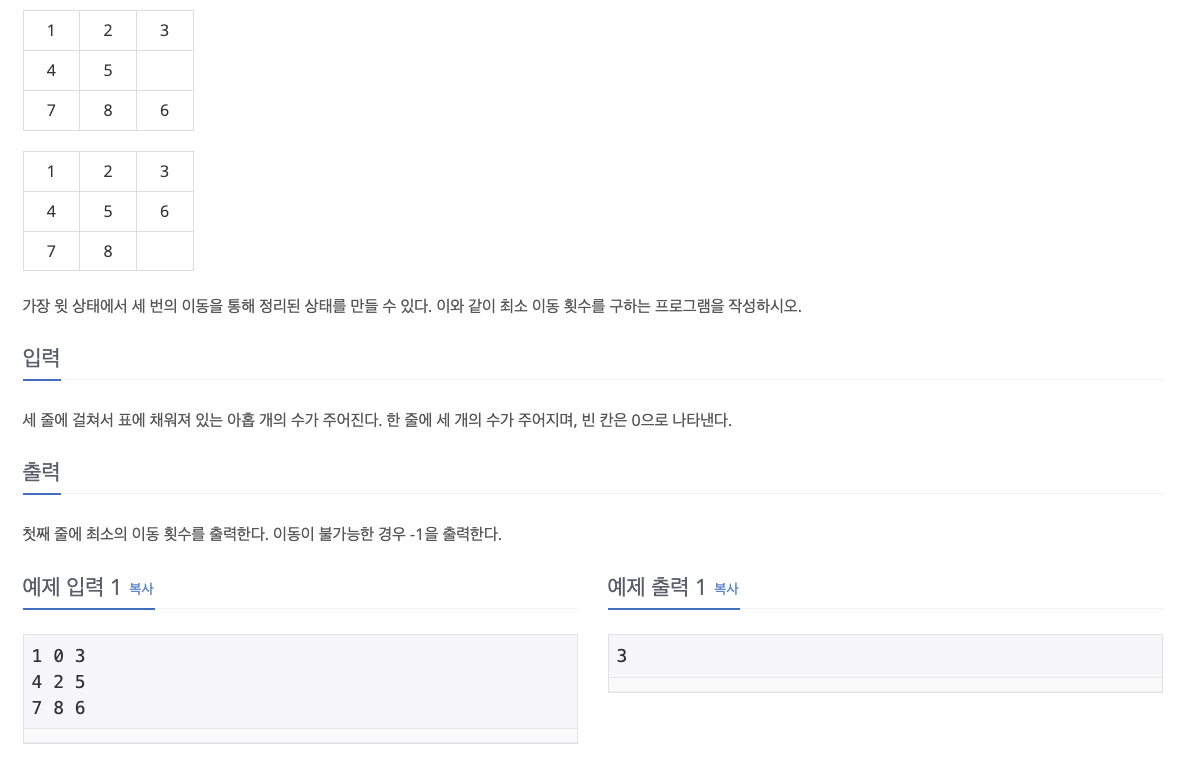
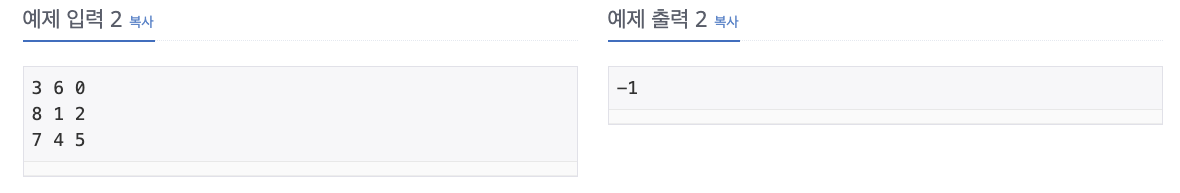
2. 풀이
2.1 풀이 방법
우선 나는 2차 배열인 퍼즐을 1차 배열로 변환하고 문제를 풀었다.
문제를 풀 때, 주어진 퍼즐의 원소를 이동시켜야 하는데 2차 배열보다는 1차 배열이 다루기 더 쉬울 거 같았기 때문이다.
2차 배열의 각 위치를 1차 배열로 표현할 수 있기 때문에 1차 배열로 변환해서 문제를 푸는데 전혀 문제가 되지 않는다.
[1차 배열로 변환]
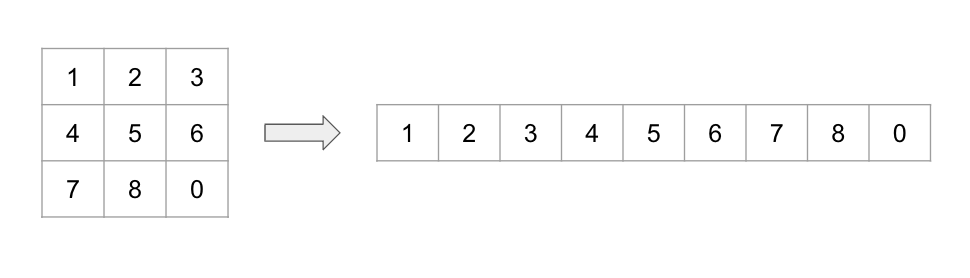
문제는 간단하다 목표 상태에 도달하기 위한 행위의 최솟값을 구하는 것이기 때문에 이 문제는 BFS를 적용해서 풀면 된다.
[퍼즐 예시]
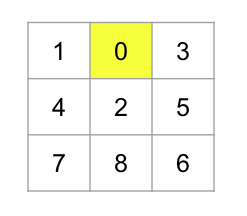
만약 퍼즐이 위와 같이 주어졌을 경우 1차 배열로 변환하면 다음과 같이 문제를 풀 수 있다.
[1차 배열로 변환 시 풀이]
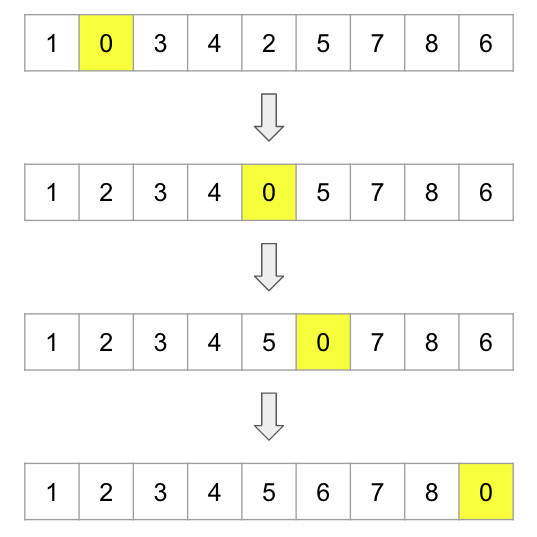
2차 배열의 퍼즐에서는 공백(0)은 상하좌우로 이동할 수 있다.
1차 배열에서는 상하좌우를 {-3, 3, -1, 1}로 표현할 수 있다.
ex) 2차 배열에서 공백(0)을 위로 이동하는 경우, 1차 배열에서 공백(0)을 현재 공백(0)의 위치에서 -3번째 위치의 값과 바꿔주면 된다.
단 공백이 1번째, 4번째, 7번째 위치에 있을 경우 좌로 이동할 수 없고, 3번째, 6번째, 9번째 위치에 있을 경우 우로 이동할 수 없다.
또한 이미 방문한 노드(퍼즐의 형태)는 다시 방문할 필요가 없기 때문에 이를 처리해주어야 한다.
나는 처음에 1차 배열의 숫자에 맞춰 방문한 노드를 체크하려고, 876543210열의 배열을 생성했지만 메모리 초과가 나버렸다.
때문에 각 노드를 맵에 저장하는 방식을 사용하였다.
ex) 103425786을 방문한 경우 맵에 (103425786, true)로 저장하고 key로 방문했는지 안 했는지를 확인
2.2 코드
[moveSet, Node]
static int[] moveSet = {-3, 1, 3, -1};
private static class Node {
int emptyLocation;
int[] numberArr = new int[9];
int count = 0;
//이동될 공백의 정보를 받아 공백을 이동시키고 퍼즐을 1차 배열로 저장
public Node(int beforeEmptyLocation, int emptyLocation, int[] numberArr, int count) {
this.count = count;
this.emptyLocation = emptyLocation;
for (int i = 0; i < numberArr.length; i++) {
this.numberArr[i] = numberArr[i];
}
int temp = this.numberArr[emptyLocation];
this.numberArr[emptyLocation] = this.numberArr[beforeEmptyLocation];
this.numberArr[beforeEmptyLocation] = temp;
}
public Node() {}
}moveSet은 1차 배열에서 공백을 이동시키기 위한 배열이다.
Node는 1차 배열로 표현된 퍼즐의 상태의 정보를 저장하는 클래스이다.
현재 공백의 위치(emptyLocation)와 퍼즐의 상태(numberArr), 현재 노드까지 이동 횟수(count)를 갖고 있다.
Node는 생성할 때 이동될 공백의 위치를 받아서 공백을 이동시키고, 이동된 상태의 퍼즐을 1차 배열로 저장한다.
[intArrToInt]
//1차 배열로 표현된 퍼즐을 Int로 변경하는 메서드
private static int intArrToInt(int[] numberArr) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : numberArr) {
stringBuilder.append(i);
}
return Integer.parseInt(stringBuilder.toString());
}1차 배열로 표현된 퍼즐을 Int로 변경하는 메서드
Int로 변경하는 이유는 bfs에서 퍼즐의 상태를 비교하거나 다루기 용이하게 하기 위함이다.
[bfs]
private static Node bfs(Node firstNode, Map<Integer, Boolean> check, int dist) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(firstNode);
//방문한 퍼즐을 map에 저장
int puzzleSet = intArrToInt(firstNode.numberArr);
check.put(puzzleSet, true);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node currentNode = queue.poll();
if (intArrToInt(currentNode.numberArr) == dist) {
return currentNode;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextEmptyLocation = currentNode.emptyLocation + moveSet[i];
//공백이 특정 위치일 때, 좌 또는 우로 이동 할 수 없기 때문에 넘어간다.
if (nextEmptyLocation < 0 || nextEmptyLocation > 8
|| (currentNode.emptyLocation % 3 == 2 & i == 1) || (currentNode.emptyLocation % 3 == 0 & i == 3)) {
continue;
}
Node nextNode =
new Node(currentNode.emptyLocation, nextEmptyLocation, currentNode.numberArr, currentNode.count + 1);
int nextPuzzleSet = intArrToInt(nextNode.numberArr);
if (check.containsKey(nextPuzzleSet)) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(nextNode);
check.put(nextPuzzleSet, true);
}
}
return null;
}BFS로 퍼즐을 맞추기까지 최소 횟수를 구하는 메서드
[main]
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
Node node = new Node();
Map<Integer, Boolean> check = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
int number = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (number == 0) {
node.emptyLocation = 3 * i + j;
}
node.numberArr[3 * i + j] = number;
}
}
Node result = bfs(node, check, 123456780);
if (result == null) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
System.out.println(result.count);
}
3. 전체 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class 퍼즐_1525 {
static int[] moveSet = {-3, 1, 3, -1};
private static class Node {
int emptyLocation;
int[] numberArr = new int[9];
int count = 0;
//이동될 공백의 정보를 받아 공백을 이동시키고 퍼즐을 1차 배열로 저장
public Node(int beforeEmptyLocation, int emptyLocation, int[] numberArr, int count) {
this.count = count;
this.emptyLocation = emptyLocation;
for (int i = 0; i < numberArr.length; i++) {
this.numberArr[i] = numberArr[i];
}
int temp = this.numberArr[emptyLocation];
this.numberArr[emptyLocation] = this.numberArr[beforeEmptyLocation];
this.numberArr[beforeEmptyLocation] = temp;
}
public Node() {}
}
//1차 배열로 표현된 퍼즐을 Int로 변경하는 메서드
private static int intArrToInt(int[] numberArr) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : numberArr) {
stringBuilder.append(i);
}
return Integer.parseInt(stringBuilder.toString());
}
private static Node bfs(Node firstNode, Map<Integer, Boolean> check, int dist) {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(firstNode);
//방문한 퍼즐을 map에 저장
int puzzleSet = intArrToInt(firstNode.numberArr);
check.put(puzzleSet, true);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node currentNode = queue.poll();
if (intArrToInt(currentNode.numberArr) == dist) {
return currentNode;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextEmptyLocation = currentNode.emptyLocation + moveSet[i];
//공백이 특정 위치일 때, 좌 또는 우로 이동 할 수 없기 때문에 넘어간다.
if (nextEmptyLocation < 0 || nextEmptyLocation > 8
|| (currentNode.emptyLocation % 3 == 2 & i == 1) || (currentNode.emptyLocation % 3 == 0 & i == 3)) {
continue;
}
Node nextNode =
new Node(currentNode.emptyLocation, nextEmptyLocation, currentNode.numberArr, currentNode.count + 1);
int nextPuzzleSet = intArrToInt(nextNode.numberArr);
if (check.containsKey(nextPuzzleSet)) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(nextNode);
check.put(nextPuzzleSet, true);
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
Node node = new Node();
Map<Integer, Boolean> check = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
int number = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (number == 0) {
node.emptyLocation = 3 * i + j;
}
node.numberArr[3 * i + j] = number;
}
}
Node result = bfs(node, check, 123456780);
if (result == null) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
System.out.println(result.count);
}
}